SGA 3
The guide reviews the design, installation, and configuration scenarios for the Streaming Gateway Appliance 3 in a Private Network with SGA deployment model for both Nutanix AHV and public cloud infrastructures. This guide assumes that the customer has an existing Frame customer or organization entity.
Introduction
SGA 3 supports both Frame Remoting Protocol (FRP) 7 and FRP8 protocols.
Network Requirements
When deploying an SGA VM, the customer's network must allow Internet traffic to reach the SGA VM and from the SGA VM to the network containing the Frame-managed workloads (e.g., Sandbox, test/production pools, Utility Servers). As a best practice, we recommend the SGA VM or VMs (if high-availability is required) be deployed in a DMZ (e.g., VPC, VNET, or VLAN), separate from the workload VM network.
Consult Public Cloud with Private Networking and SGA or Nutanix AHV with Private Networking and SGA to ensure that network routing requirements are satisfied before continuing to installation and configuration.
SGA 3 does not support IPv6 addresses.
High Availability
- FRP7
- FRP8
Customers who wish to implement a high availability SGA solution must use a third-party load balancer. The load balancer is placed in front of one or more SGA VMs. These SGA VMs will act as the pool of SGA VMs ("SGA VM Pool") that will handle the FRP7 session traffic between end users and the Frame workload VMs.
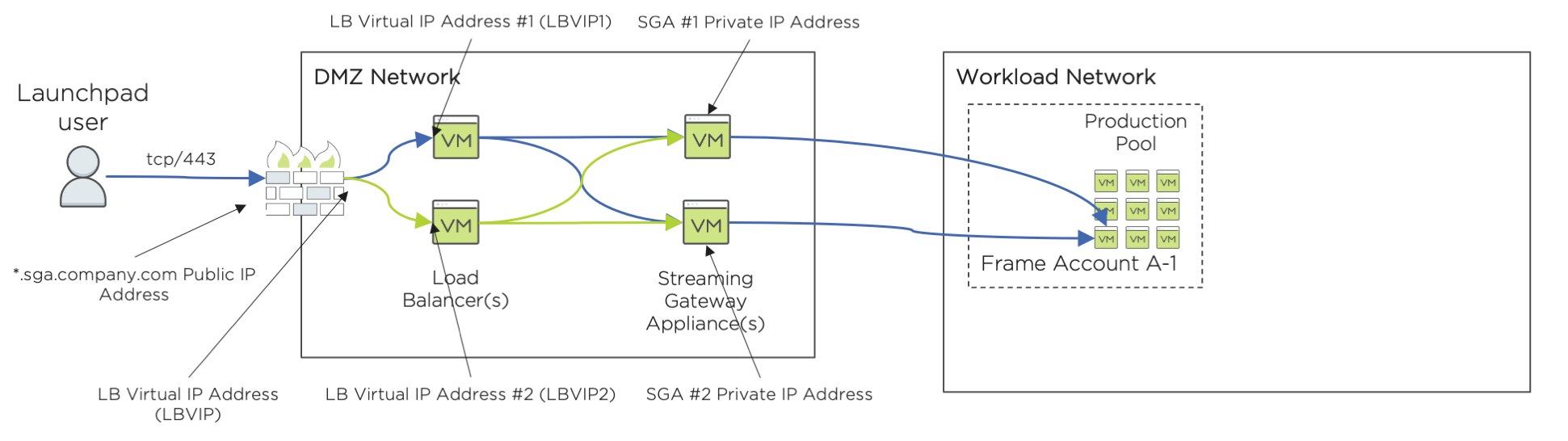
The environment will need the following:
- A wildcard DNS A record, publicly resolvable via
*.sga.company.comwildcard FQDN to a public IP address on the firewall ("SGA Farm Virtual Public IP Address") - A private IP address on the load balancer ("SGA Farm Virtual Private IP Address", noted as "LBVIP" in the above diagram)
- The SGA Farm Virtual Public IP Address network address translated (NAT) to the SGA Farm Virtual Private IP Address (LBVIP) on the load balancer.
- Load balancer configured to:
- Assign inbound
tcp/443(HTTPS, WSS) request to a specific SGA VM in the SGA VM Pool. - Terminate the TLS connection on the assigned SGA VM and not the load balancer (SSL Passthrough).
- Use SSL Persistence (SSL Session ID) to persist the HTTPS/WSS Frame session on a specific SGA VM.
- Assign inbound
Customer must prevent the load balancer from switching a user's Secure WebSocket connection (when using FRP7) from one SGA VM to another SGA VM. Switching of the Secure WebSocket connection while a user is in a FRP7 session may cause the session to disconnect (and potentially close) and require the end user to resume their session (or start a new session).
Typical FRP7 Workflow
A Frame user logs in to the Frame Platform and is directed to their Launchpad. When the user clicks the desktop or application icon in their Launchpad, Frame Platform directs the user's browser to an FQDN based on the SGA subdomain, as configured by Frame Support, for the Frame account.
For example, if the subdomain was sga.company.com and the workload VM had a private IP address of 10.2.1.3, the workload FQDN would be 10-2-1-3.sga.company.com. This workload FQDN resolves from the customer's public DNS server to the public IP address on the customer's firewall. The firewall performs NAT and sends the request to the virtual SGA IP address (LBVIP). One of the load balancers receives the HTTPS request and forwards the request to one of the SGA VMs. The SGA VM then forwards the HTTPS request to the user's assigned Frame workload VM and Frame Agent on the workload VM validates the session start request and switches to a Secure WebSocket connection to begin the Frame session video/audio stream.
The load balancer is configured to keep the HTTPS/Secure WebSocket connection between the end user and the assigned SGA VM.
Customers who wish to implement a high availability SGA solution must use a third-party load balancer. The load balancer is placed in front of one or more SGA VMs. These SGA VMs will act as the pool of SGA VMs ("SGA VM Pool") that will handle the FRP8 session traffic between end users and the Frame workload VMs.
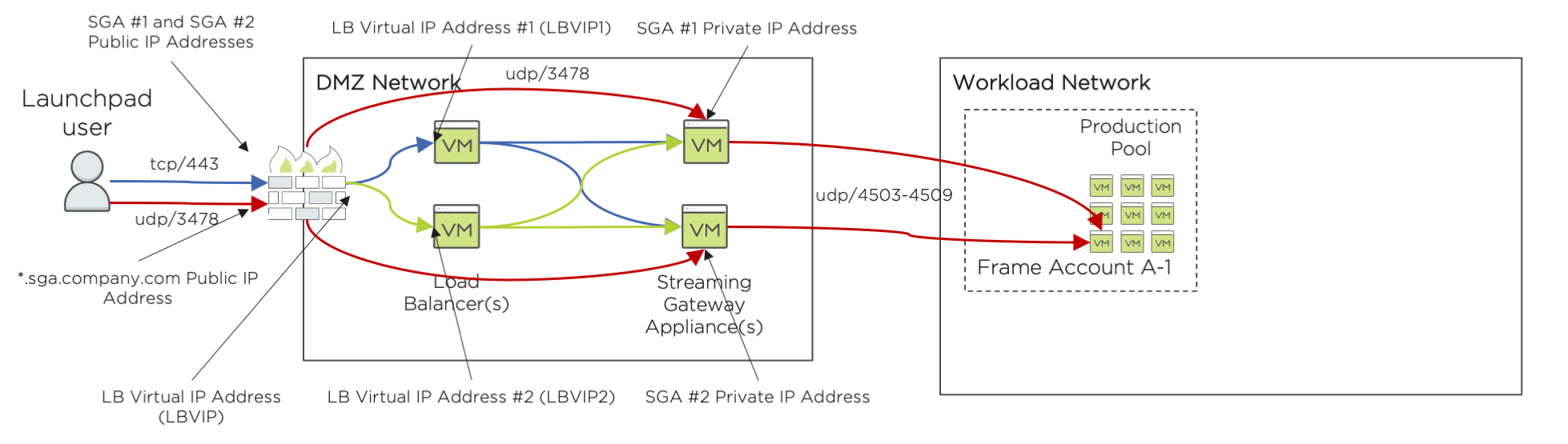
The environment will need the following:
- A wildcard DNS A record, publicly resolvable via
*.sga.company.comwildcard FQDN to a public IP address on the firewall ("SGA Farm Virtual Public IP Address") - A private IP address on the load balancer ("SGA Farm Virtual Private IP Address", noted as "LBVIP" in the above diagram)
- The SGA Farm Virtual Public IP Address network address translated (NAT) to the SGA Farm Virtual Private IP Address (LBVIP) on the load balancer.
- Load balancer configured to:
- Assign inbound
tcp/443(HTTPS, WSS) request to a specific SGA VM in the SGA VM Pool. - Terminate the TLS connection on the assigned SGA VM and not the load balancer (SSL Passthrough).
- Use SSL Persistence (SSL Session ID) to persist the HTTPS/WSS Frame session on a specific SGA VM.
- Assign inbound
- Each SGA VM has its own public IP address mapped to the SGA VM's private IP address (destination network address translation - DNAT). Once the load balancer assigns a SGA VM to an end user to start their FRP8 session, the FRP8
udp/3478andtcp/3478(optional) traffic from the end user's device to the specific SGA VM (and vice versa) does not go through the load balancer. - For each SGA VM, the destination public IP address for ingress traffic to the SGA VM is the same public IP address as the source public IP address for egress traffic from the SGA VM to the Internet. Each SGA VM's egress traffic cannot be source network address translated (SNAT) to a different public IP address.
- Each SGA VM will forward FRP8 traffic to the user's assigned Frame workload VM using
udp/4503-4509.
Customer must ensure that the load balancer only load balances on ingress tcp/443 (HTTPS) traffic. The load balancer must not load balance ingress udp/3478 or tcp/3478 FRP8 traffic from the end users' devices to the load balancer-assigned SGA VMs.
Typical FRP8 Workflow
A Frame user logs in to the Frame Platform and is directed to their Launchpad. When the user clicks the desktop or application icon in their Launchpad, Frame Platform directs the user's browser to an FQDN based on the SGA subdomain, as configured by Frame Support, for the Frame account.
For example, if the subdomain was sga.company.com and the workload VM had a private IP address of 10.2.1.3, the workload FQDN would be 10-2-1-3.sga.company.com. This workload FQDN resolves from the customer's public DNS server to the public IP address on the customer's firewall. The firewall performs NAT and sends the request to the virtual SGA IP address (LBVIP). One of the load balancers receives the HTTPS request and forwards the request to one of the SGA VMs.
The SGA VM responds to the user's HTTPS request with an HTTPS response specifying the public IP address the user's browser or Frame App must use to continue the FRP8 session. This SGA VM public IP address was obtained by the SGA VM through a WebRTC STUN request (udp/3478) to Frame control plane endpoint stun.console.nutanix.com.
The user's browser or Frame App begins communicating directly with the specific SGA VM using the provided public IP address using udp/3478 (or tcp/3478 if configured by the administrator). The SGA VM then forwards the FRP8 traffic to the user's assigned Frame workload VM using udp/4503-4509. The Frame Agent on the workload VM validates the session start request and begin the Frame session video/audio stream.
Internal Access to SGA-enabled Workloads
Frame administrators may want end users within their private network to access the workloads of an SGA-enabled Frame account at the same time users on the Internet are accessing workloads in the same Frame account. When a Frame account is configured to rely on an SGA, all end users using workload VMs in the Frame account are provided the SGA FQDN by the Frame control plane.
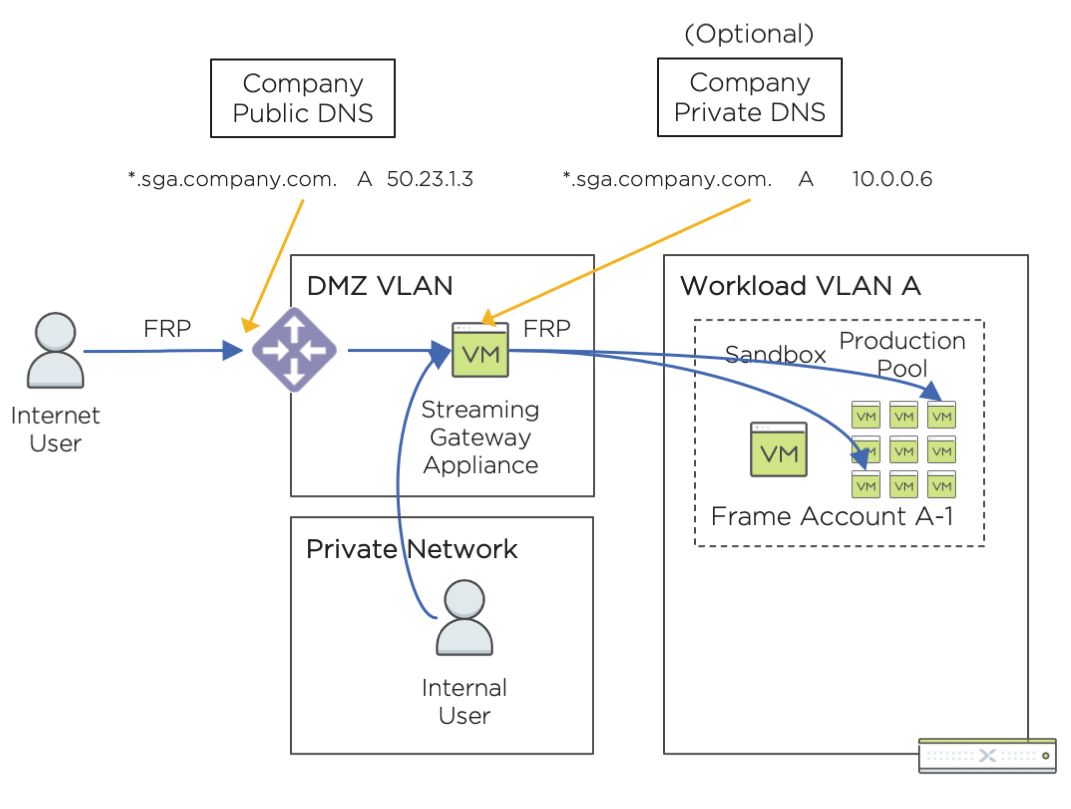
To enable end users on your private network to use the SGA-enabled Frame account, determine whether end users on your internal network are able to go to the public IP address associated with the wildcard FQDN of your SGA. If your internal end users cannot reach the public IP address of the wildcard FQDN of your SGA, then configure your internal DNS servers to return the private IP address of the SGA VM (or the virtual private IP address of the SGA on your load balancer) for the SGA subdomain. Simply add the SGA subdomain as a wildcard DNS A record in your private DNS server as you did in your public DNS server.
Depending on your network security policies, you may need to update your firewall rules so end users on your private network can reach the SGA VMs. Refer to the network configuration requirements for Public Cloud with Private Networking and SGA, or Nutanix AHV with Private Networking and SGA, row “End user to SGA” for the specific protocols and ports that must be allowed to the SGA VM or the load balancer (if more than one SGA VM). The source IP address of the end user's endpoint would be private IP addresses, instead of a public IP address.
Multi-Frame Account Support
A manually-deployed SGA can be configured to serve as the reverse proxy for multiple Frame accounts.
When providing the Frame workloads VLAN CIDR in the SGA Toolbox, specify a CIDR value that covers the CIDRs for the individual Frame accounts. For example, if Frame Account #1 uses 10.0.0.0/24 and Frame Account #2 users 10.0.1.0/24, then specify a CIDR of 10.0.0.0/23 for the SGA.